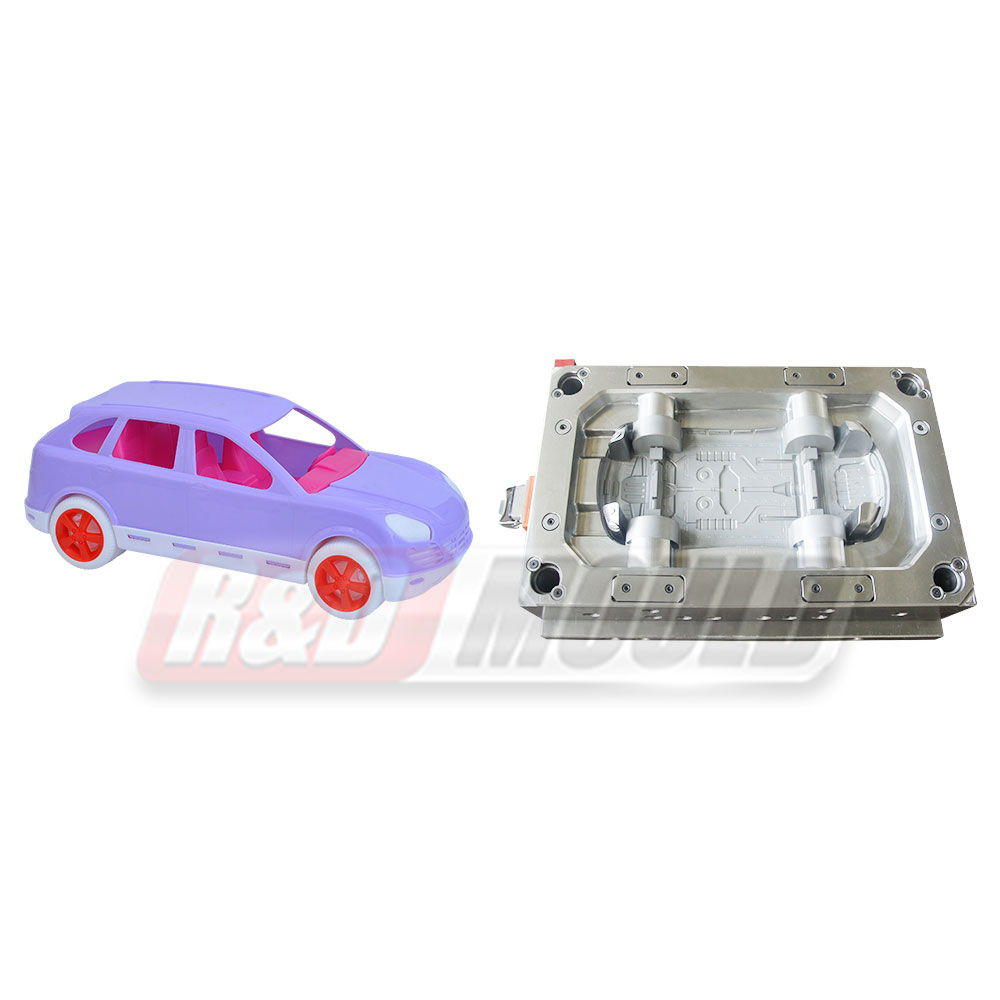
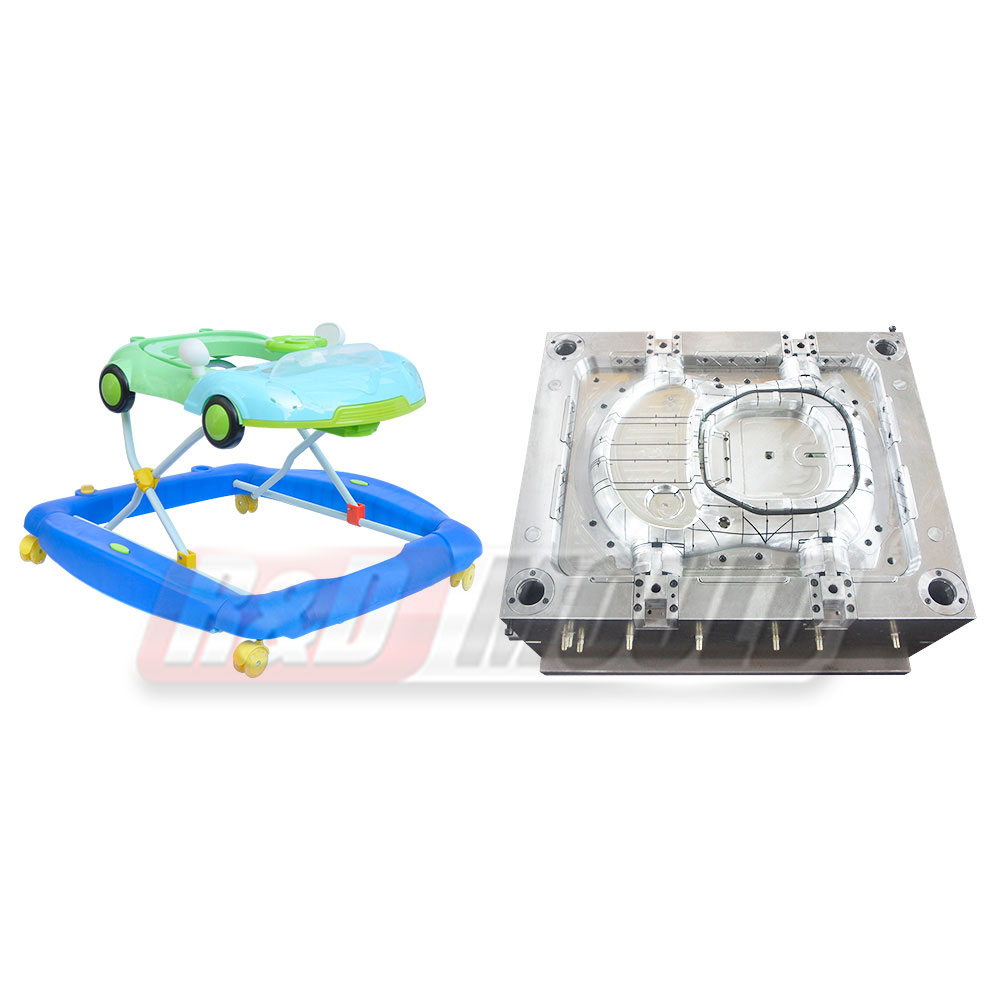
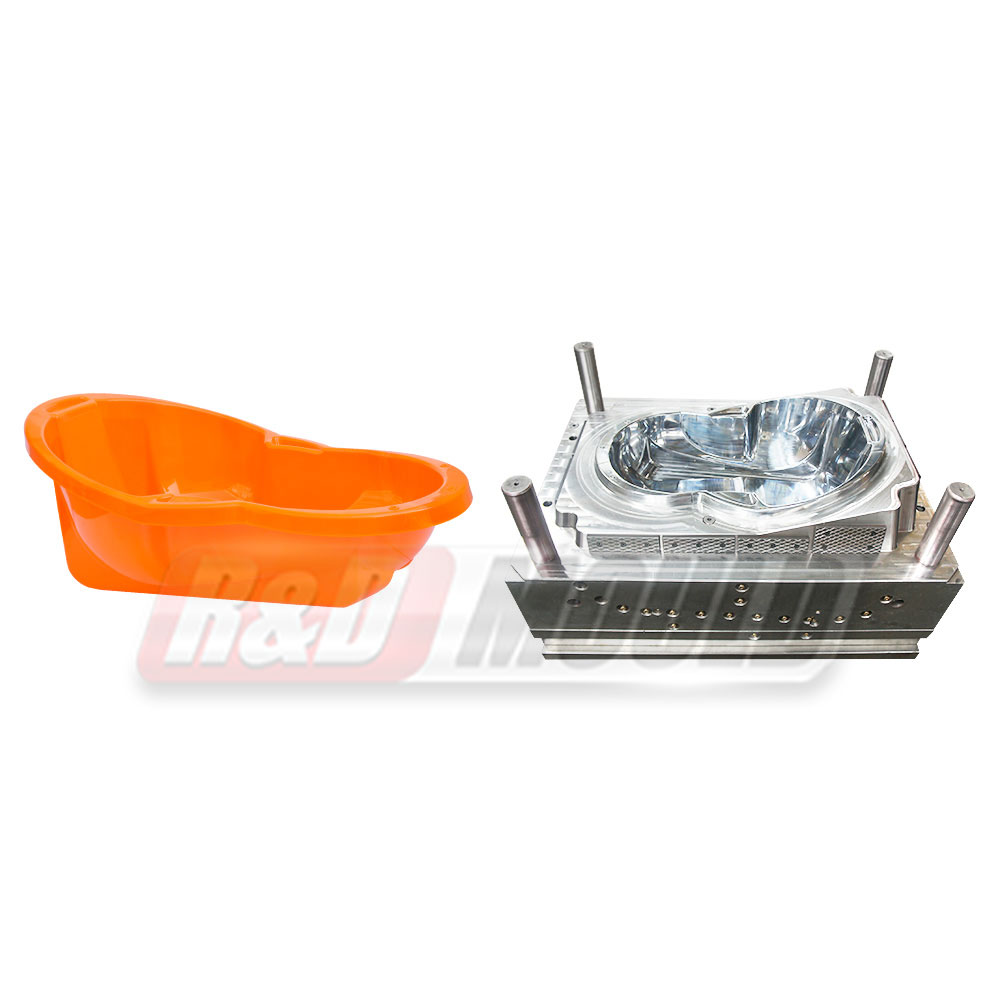
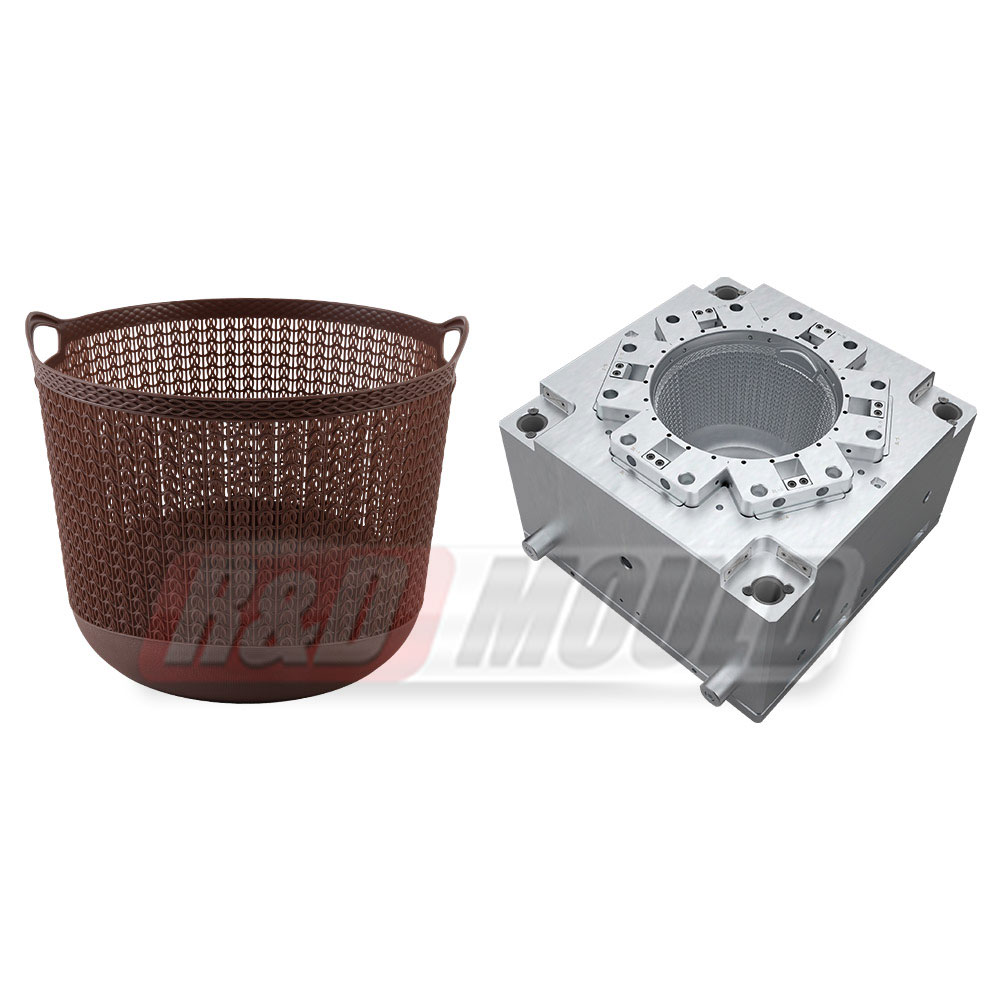
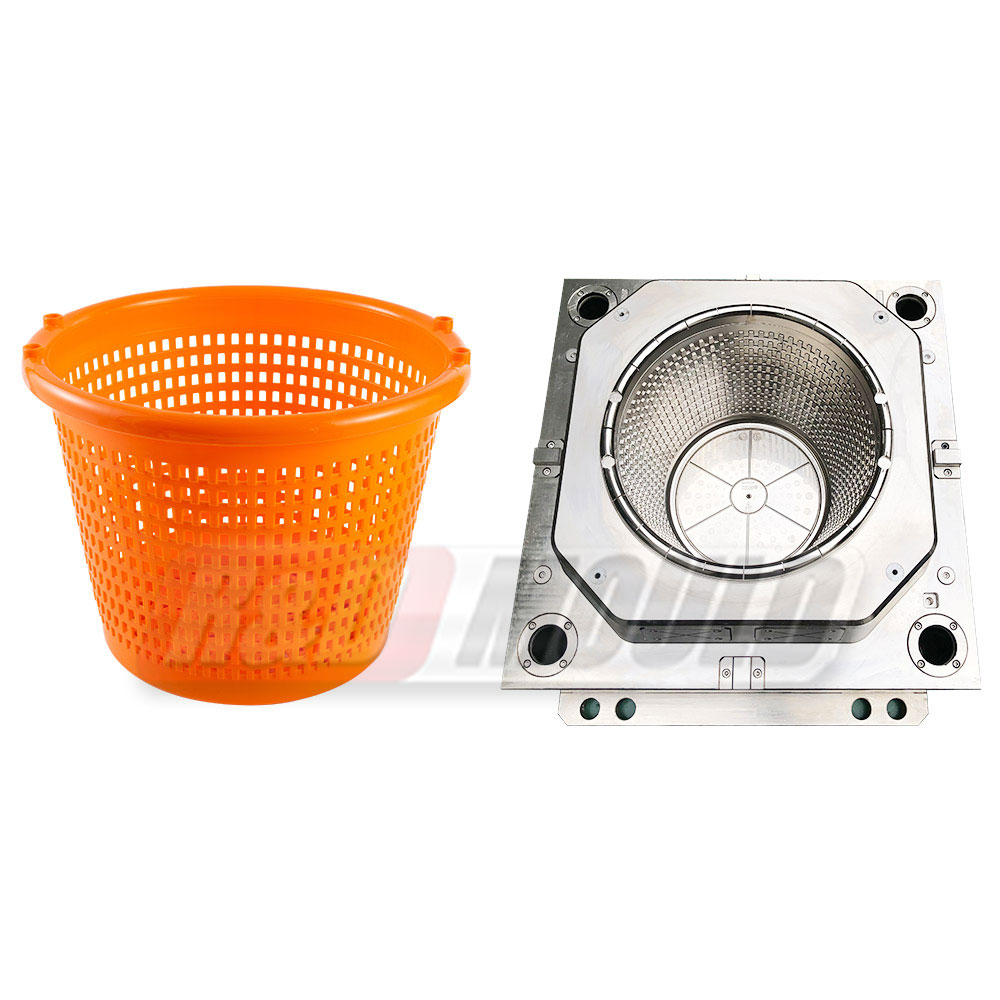
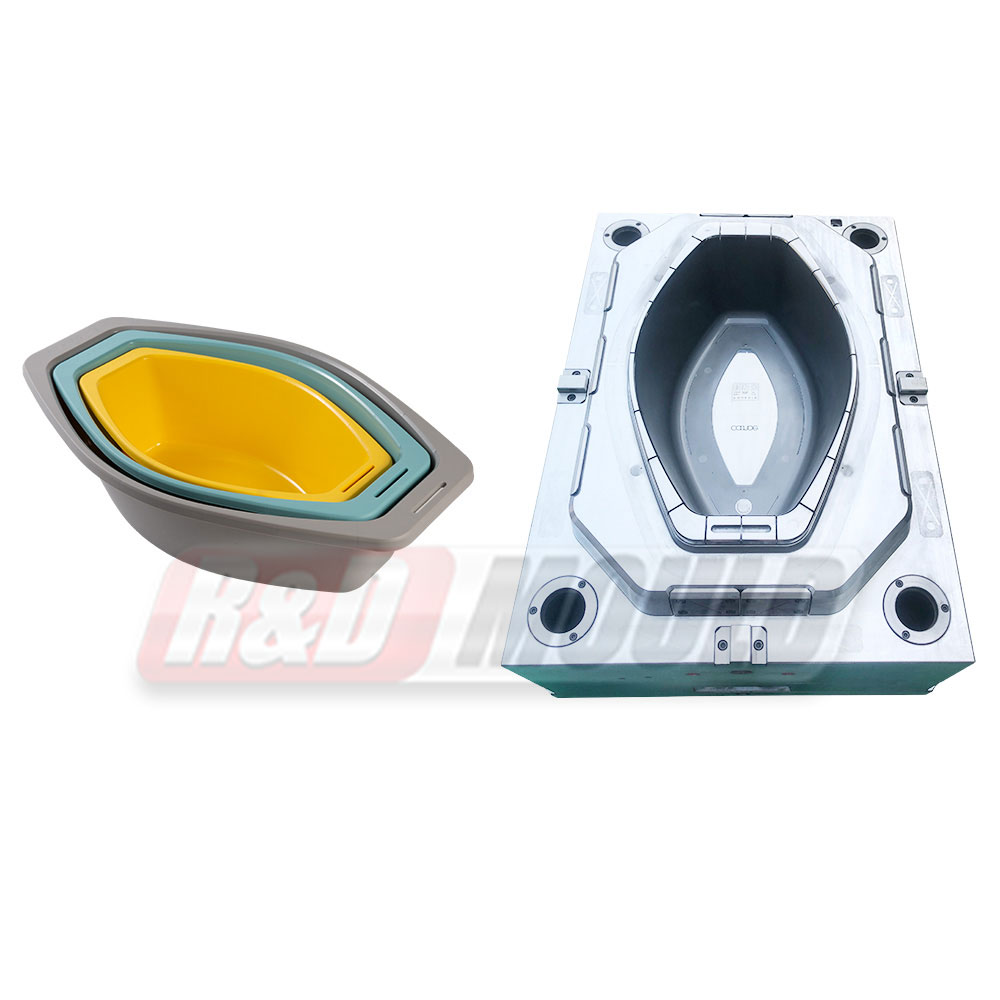
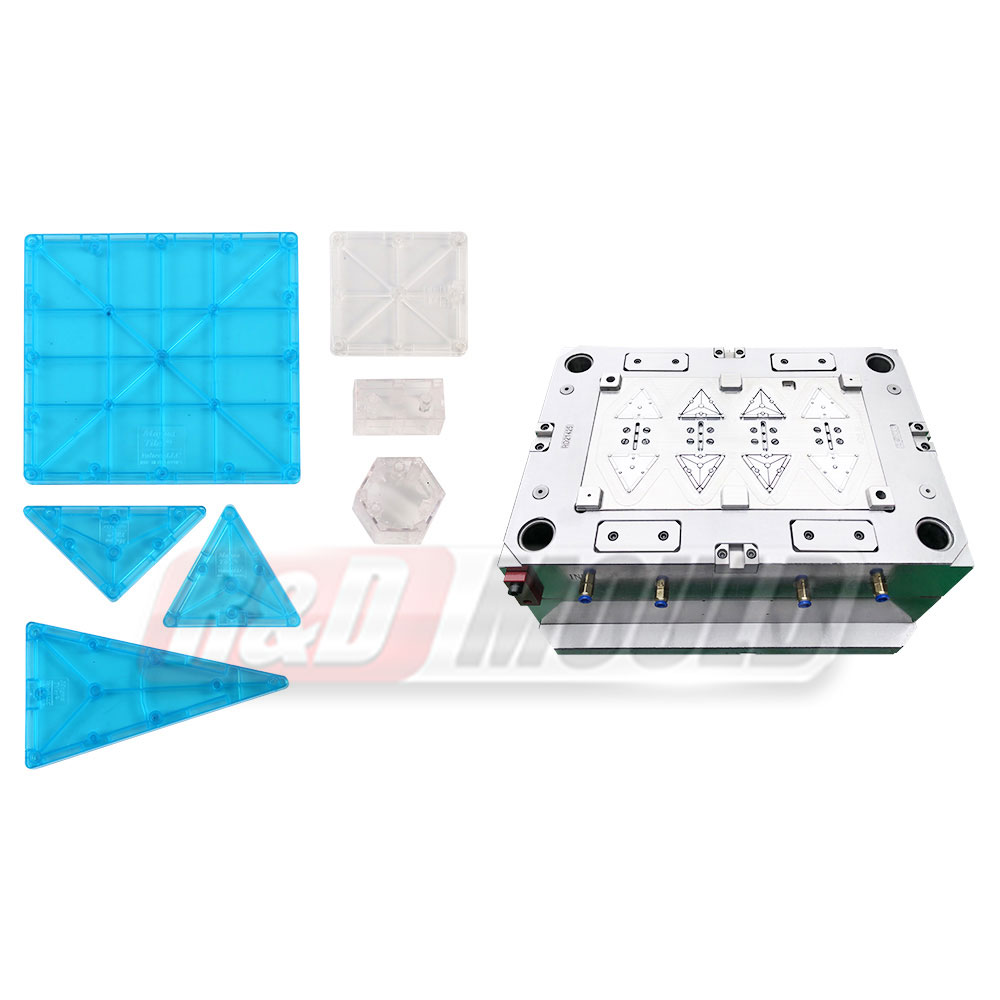
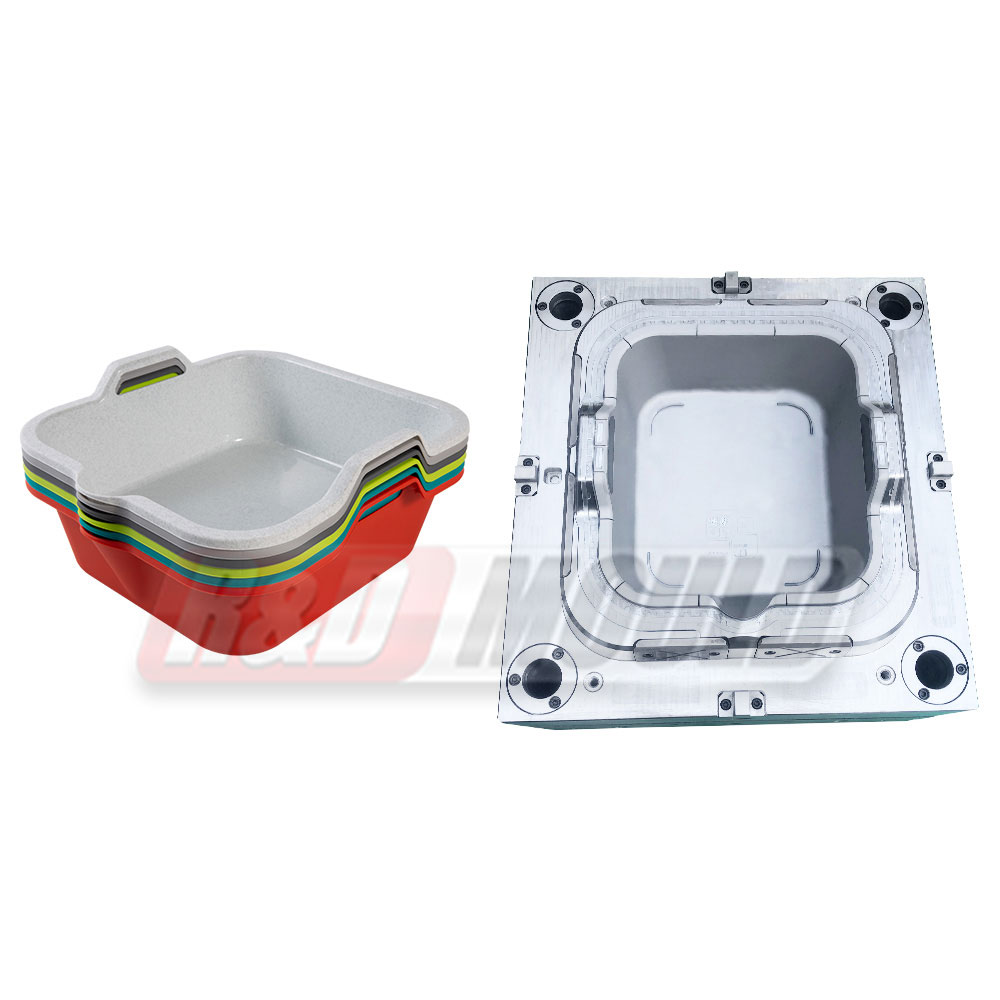
In the highly competitive packaging industry, the role of precision engineering in Food Container Mould development cannot be overstated. As demand for durable, lightweight, and cost-effective food containers rises, manufacturers are investing heavily in the refinement of Food Container Mould technologies. From design intricacies to advanced production methods, the process is becoming increasingly sophisticated to meet modern market requirements.
One of the core components of effective Food Container Mould development lies in understanding and applying key parameters during the design phase. Precision in aspects like draft angles, cooling systems, and parting line layout significantly affects the efficiency of the mould and the quality of the final product. A proper draft angle in a Food Container Mould ensures smooth ejection of the container, reducing wear on the mould and minimising defects. Even a slight miscalculation in draft angle can cause sticking, to production delays and added maintenance.
Another essential parameter in Food Container Mould design is the optimisation of the cooling system. An efficient cooling layout shortens the cycle time, which directly translates into increased productivity. Water channels must be strategically placed to ensure even temperature distribution, avoiding warping or stress concentration. Especially in thin-wall applications, the cooling configuration within a Food Container Mould becomes a defining factor for dimensional accuracy and strength.
Equally important is the design of the parting line—the boundary at which two mould halves meet. In a Food Container Mould, this line must be positioned in a way that does not compromise the integrity or aesthetics of the container. A well-conceived parting line prevents flash formation and ensures seamless product release, which is vital for maintaining visual appeal and functional performance.
As technology progresses, 3d printing has begun reshaping how Food Container Moulds are developed. Additive manufacturing allows for rapid prototyping, enabling design validation at a fraction of the time and cost of traditional methods. Engineers can now test multiple iterations of a Food Container Mould design quickly, gaining valuable feedback before committing to full-scale production. Additionally, 3d printing offers the potential to create complex geometries and conformal cooling channels, which were previously difficult or impossible to manufacture using conventional machining.
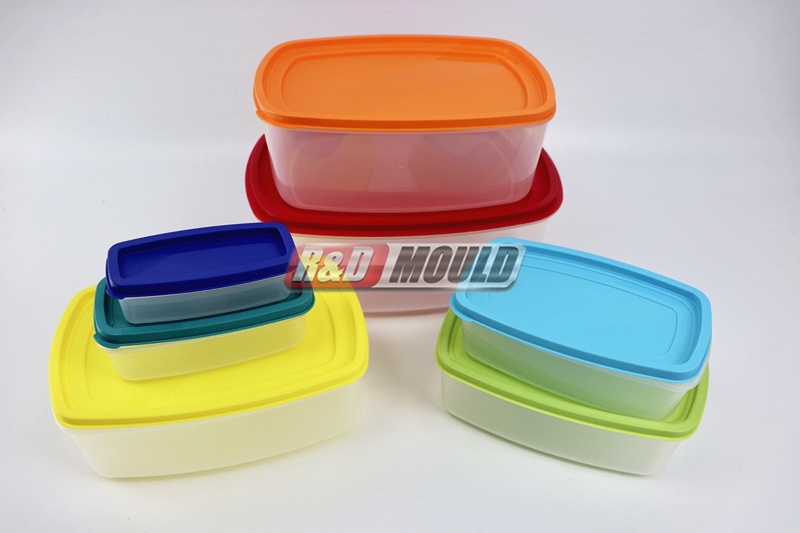

In the realm of Food Container Mould production, traditional machining methods still hold a crucial role. CNC machining offers high precision and repeatability, which is essential for producing cavity and core components of a Food Container Mould. CNC systems interpret complex CAD data to carve intricate details from hardened steel or aluminium, ensuring each mould segment meets tight tolerances.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) further enhances the Food Container Mould manufacturing process, particularly when working with hard metals or intricate features. By using electrical sparks to erode material, EDM can shape areas that conventional cutting tools struggle to reach. This makes it ideal for finishing sharp corners or deep cavities within a Food Container Mould.
Laser engraving has also gained traction in mould production, especially for branding and traceability. With laser precision, manufacturers can etch logos, batch numbers, or expiry indicators directly onto the Food Container Mould, streamlining the downstream packaging process. This not only improves product traceability but also adds a professional finish to each container.
As Food Container Mould technology continues to evolve, manufacturers are also paying greater attention to material selection. High-performance steels and surface treatments like nitriding or PVD coatings are now standard in premium Food Container Moulds. These advancements extend tool life and improve resistance to wear and corrosion, ensuring consistent output over prolonged production runs.
Sustainability is another growing consideration. The ability to produce lightweight containers with thinner walls, without compromising strength, is a direct result of improvements in Food Container Mould design and manufacturing. Efficient moulds reduce material waste, optimise energy use, and contribute to more eco-conscious production cycles.
In conclusion, the landscape of Food Container Mould production is being transformed by a synergy of traditional expertise and emerging technologies. By focusing on precision design, optimising thermal dynamics, and embracing additive manufacturing, the industry is moving towards faster, cleaner, and more flexible production models. Each advancement brings us closer to more sustainable, reliable, and innovative solutions in food packaging, with the Food Container Mould remaining at the heart of it all.



 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español Français
Français