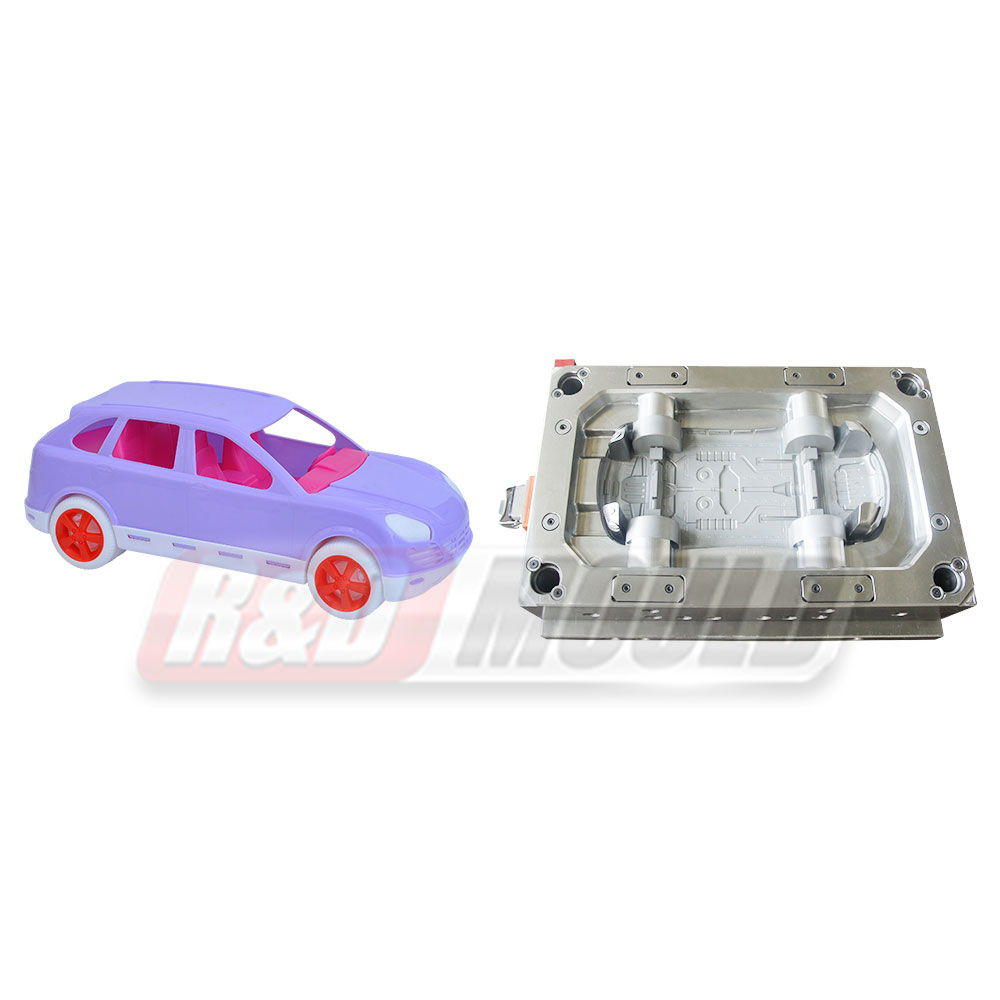
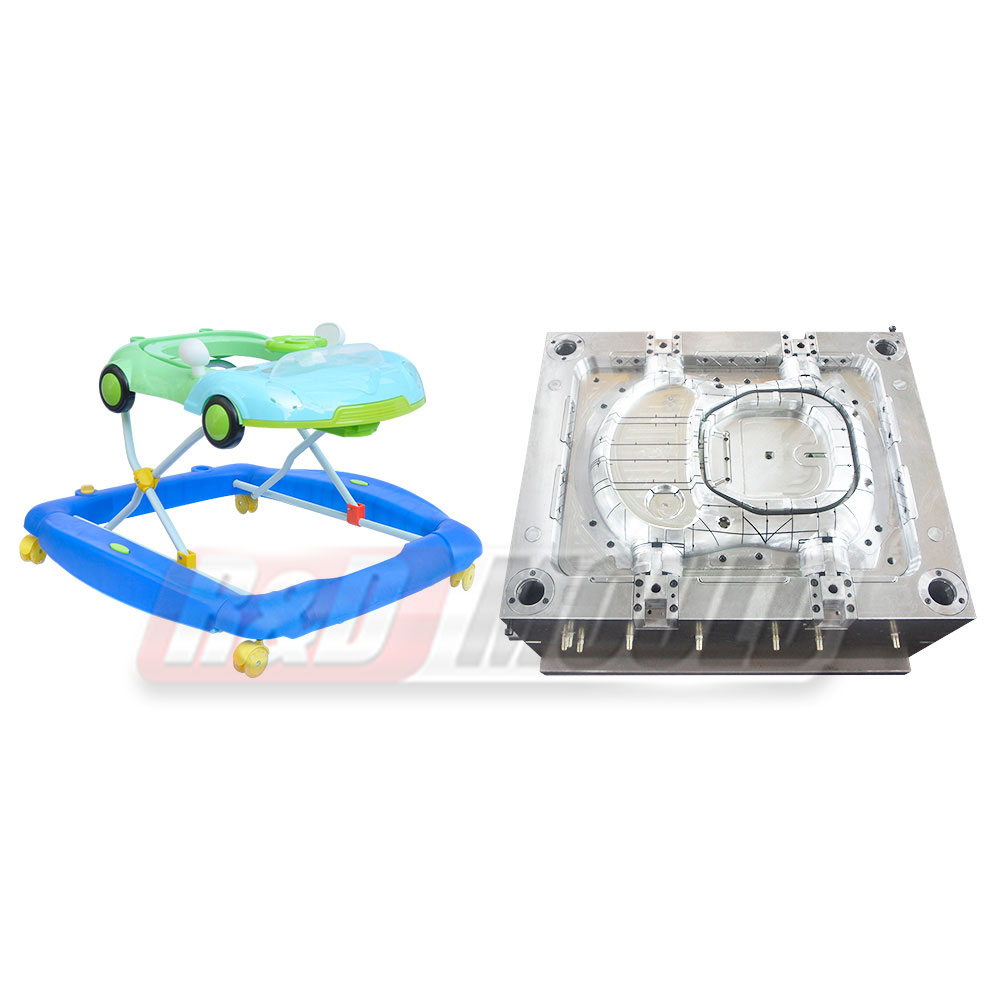
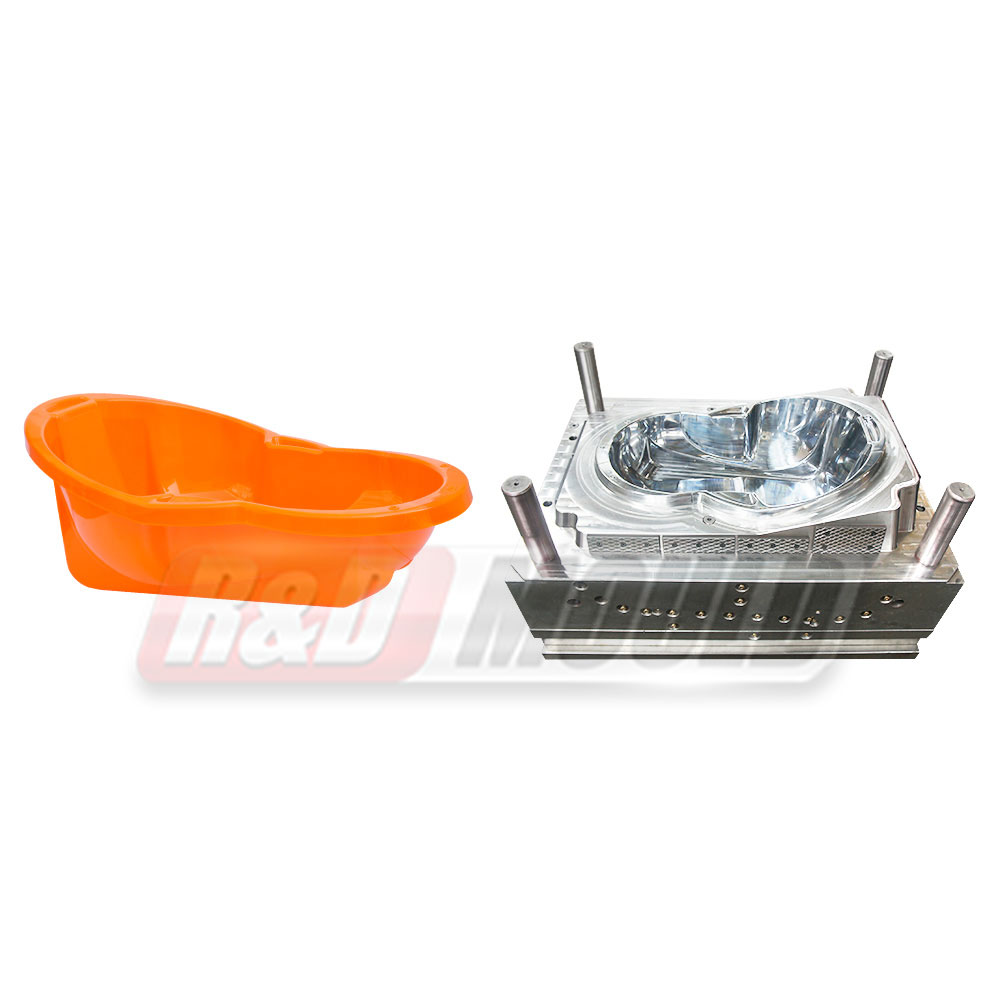
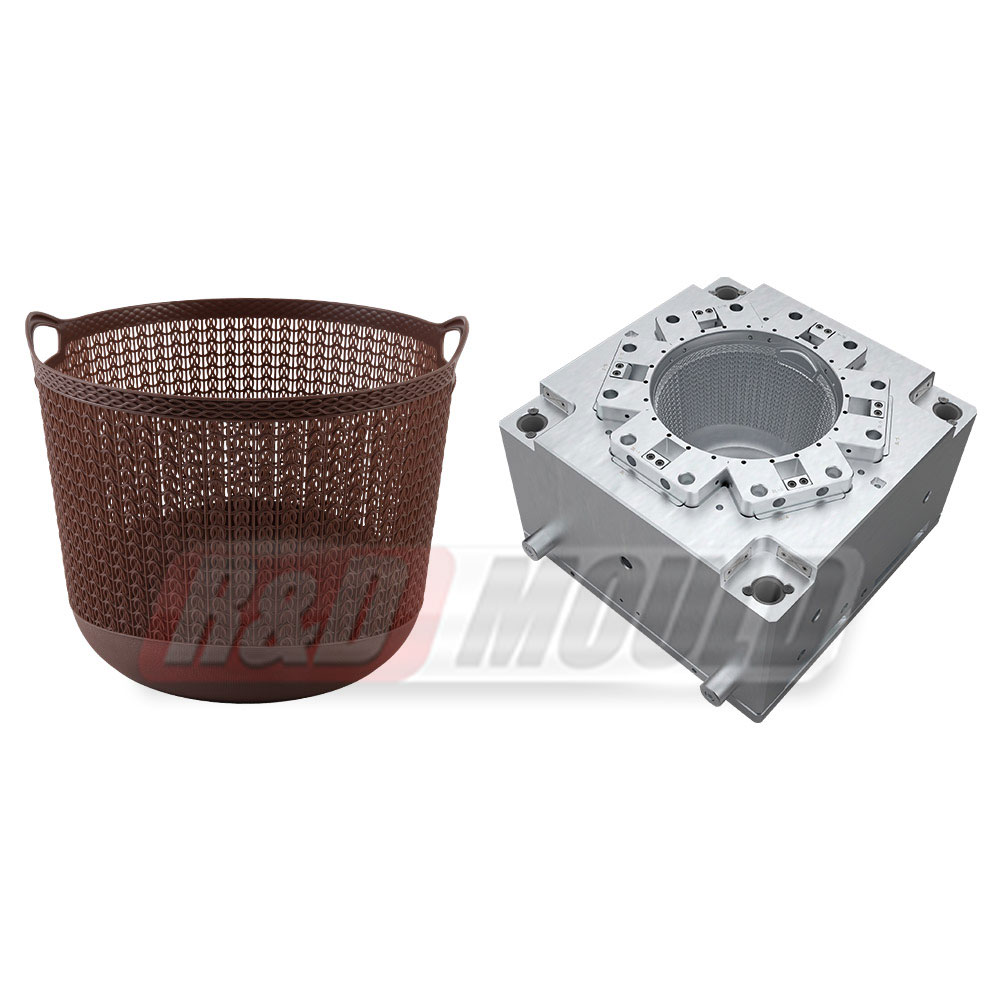
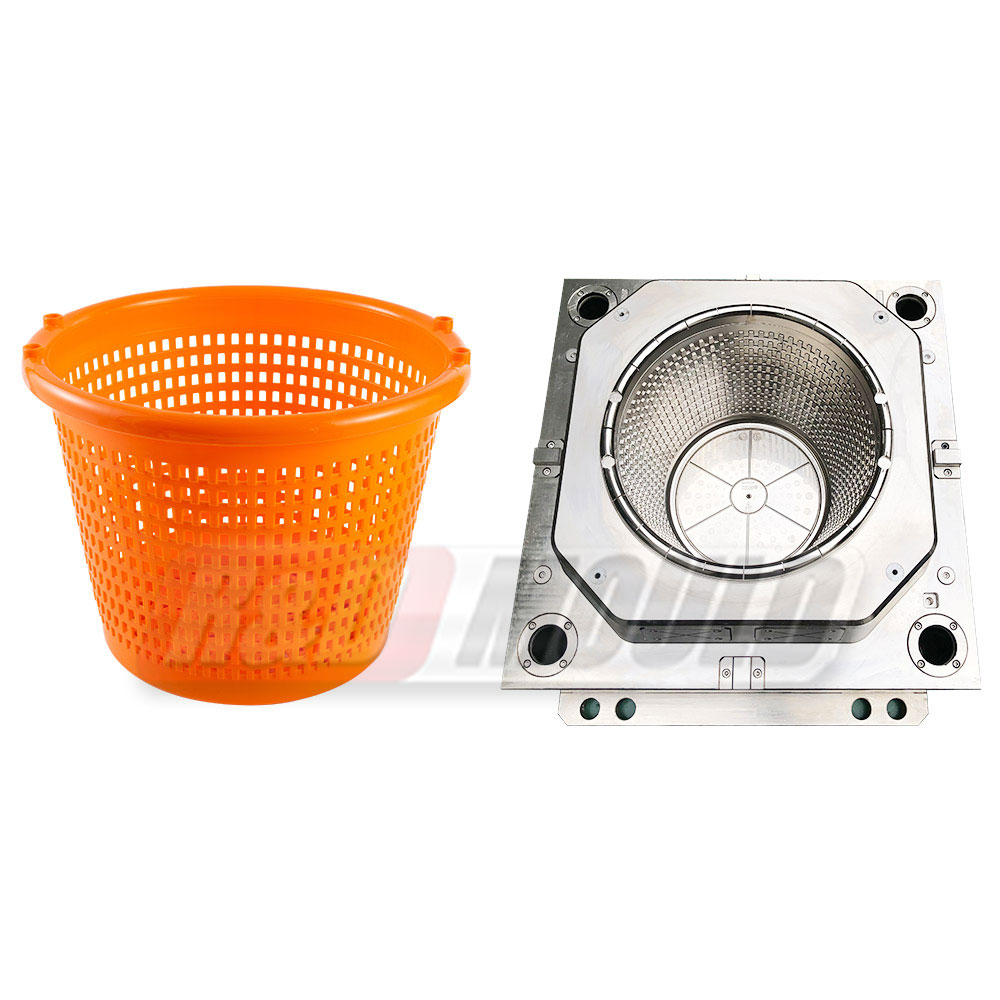
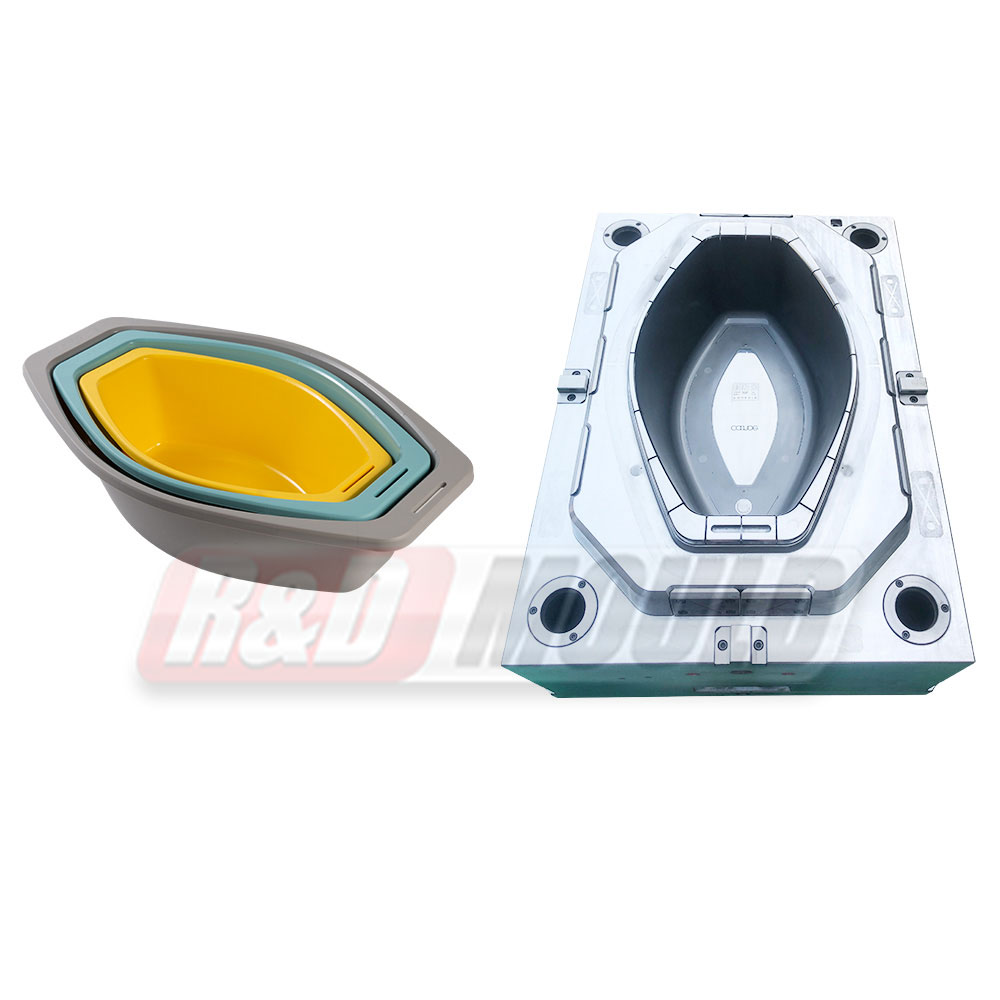
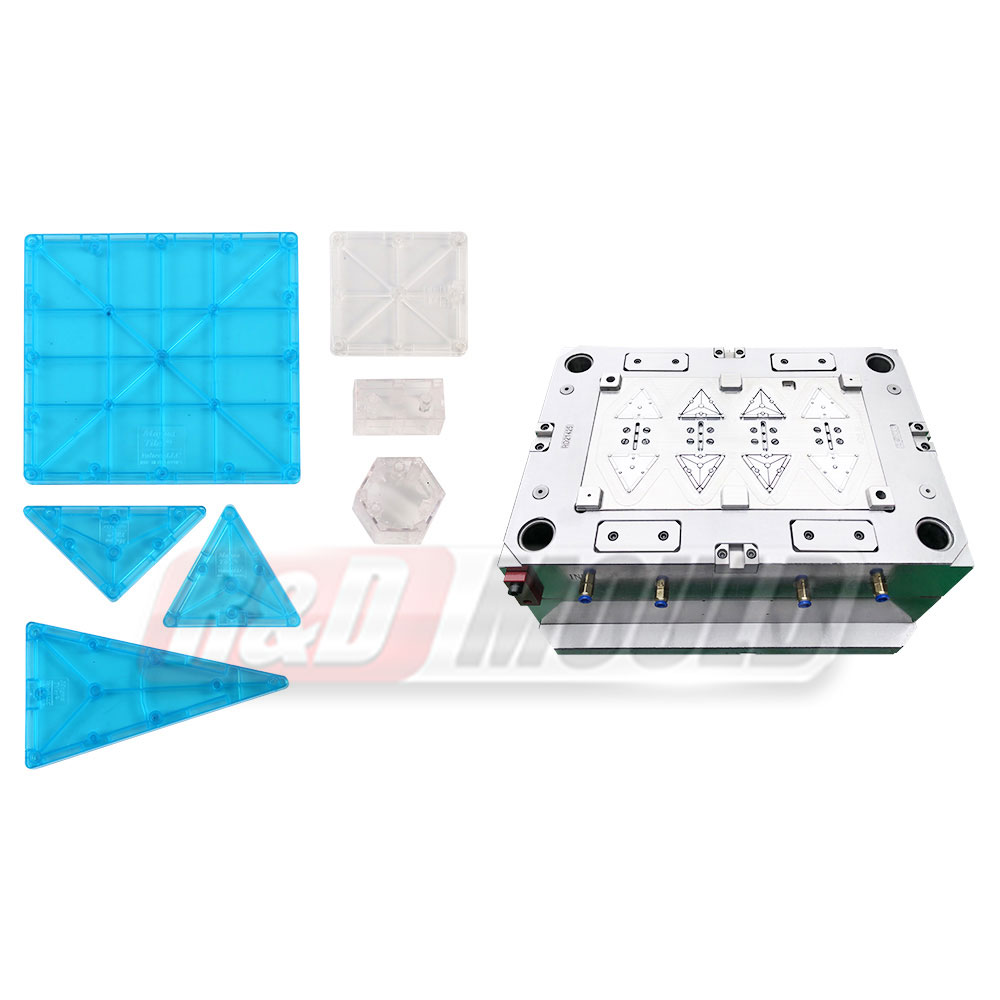
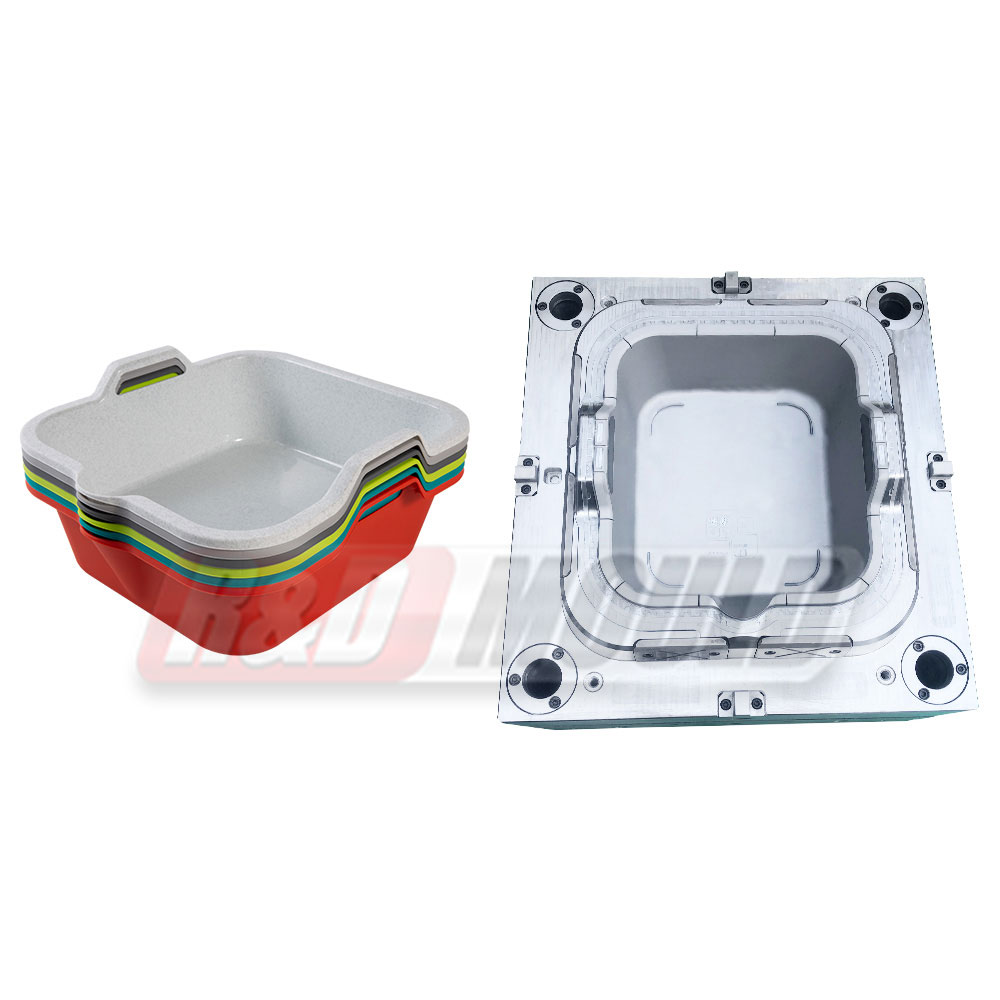
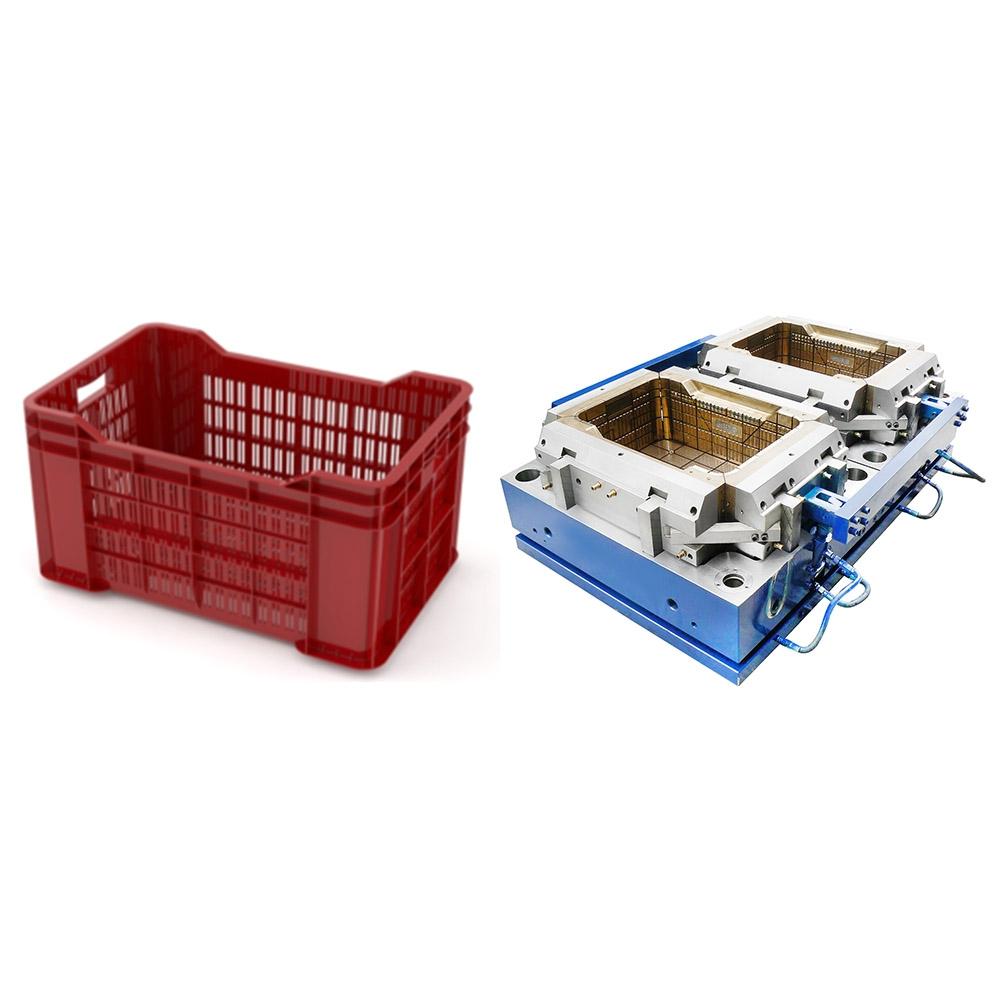
Crate molds are essential tools in the production of durable plastic crates used in logistics, storage, and retail industries. Many manufacturers and designers often have questions about lead times, materials, design considerations, cooling, and mold efficiency. This article addresses some of the most frequently asked questions about crate molds.
How Long Does It Take to Produce a Crate Mold?
The production time for a crate mold can vary depending on several factors. Generally, it takes 6 to 12 weeks from initial design to delivery. Factors influencing lead time include the complexity of the crate design, the number of cavities in the mold, and the precision required for surface finishes. For instance, crates with reinforced corners, integrated handles, or textured surfaces may require additional machining and testing, which can extend production time. Clear communication between the mold maker and client during the design phase helps streamline the process and avoid delays.

Which Materials Are Suitable for Crate Molds?
Material selection is crucial for the durability and performance of a crate mold. Common materials include P20, H13, and S136 tool steels, which offer hardness, wear resistance, and longevity under repeated injection cycles. Stainless steel may be used when corrosion resistance is a priority. Aluminum is an option for prototype or low-volume crate molds because it is easier to machine and more cost-effective, though it wears faster during high-volume production.
How Do Wall Thickness and Part Design Affect Performance?
The design of the crate significantly influences mold performance. Maintaining a uniform wall thickness is essential to reduce sink marks, warping, and uneven cooling. Typical wall thickness ranges from 2 to 5 millimeters, depending on crate size and load requirements. Handles, corners, and stacking ribs need careful design to avoid stress concentrations. Smooth transitions between thick and thin sections, along with proper draft angles, ensure easier ejection from the crate mold and prevent part damage.
How Does Cooling Design Affect Crate Mold Quality?
Cooling design is one of the most important factors in crate mold quality. Efficient cooling reduces cycle time, ensures uniform part dimensions, and minimizes residual stress. Traditional straight-drilled channels are widely used, but conformal cooling channels can provide even better results. These channels follow the shape of the crate walls, ensuring uniform temperature distribution in complex areas such as handles or reinforced corners. Proper cooling design improves surface finish, reduces warping, and enhances mold longevity.
How Should Gates and Vents Be Placed in Crate Molds?
Proper gate and vent placement ensures smooth filling of the crate mold and prevents defects. Gates are usually positioned in thicker areas to maintain a uniform flow of molten plastic. Critical zones, such as handles, corners, and deep ribs, often require vents to release trapped air and avoid burn marks or incomplete filling. For multi-cavity crate molds, flow balance is essential to ensure all cavities fill simultaneously and maintain consistent part quality.
Understanding the production process, material selection, design considerations, cooling, and venting strategies is essential for achieving high-quality crate molds. Careful attention to these factors ensures efficient production, durable molds, and reliable performance for industrial and commercial applications. Advanced techniques, such as conformal cooling channels, combined with thoughtful gate and vent placement, can further improve crate mold efficiency and product quality.
By addressing these frequently asked questions, manufacturers and designers can make informed decisions that optimize both crate mold performance and the quality of the final plastic crates.



 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español Français
Français