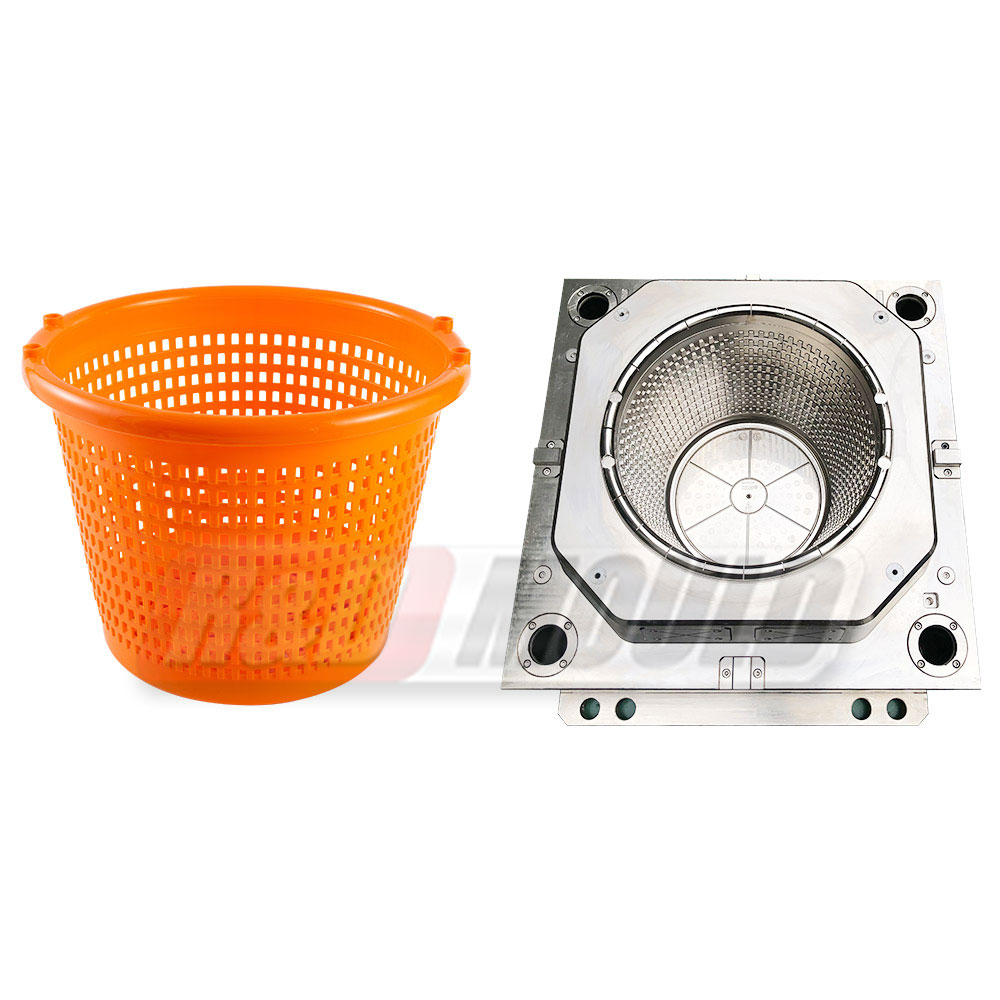
Plastic crates are widely used in storage, assembly, and transportation across many industries. They are expected to handle repeated loading, stacking, and movement without cracking or deformation. These practical demands place clear requirements on CrateMould design, especially around structural strength, surface quality, and mould durability.
Unlike lightweight household items, crates often carry concentrated loads. Handles, bottom ribs, and corner areas receive repeated stress. If these areas are not well designed at the mould stage, problems usually appear during real use rather than during mould trials.
A practical Crate Mold Manufacturer focuses on how the crate behaves after leaving the factory, not just how it looks after injection.
Common Crate Mould Types and Their Structural Differences
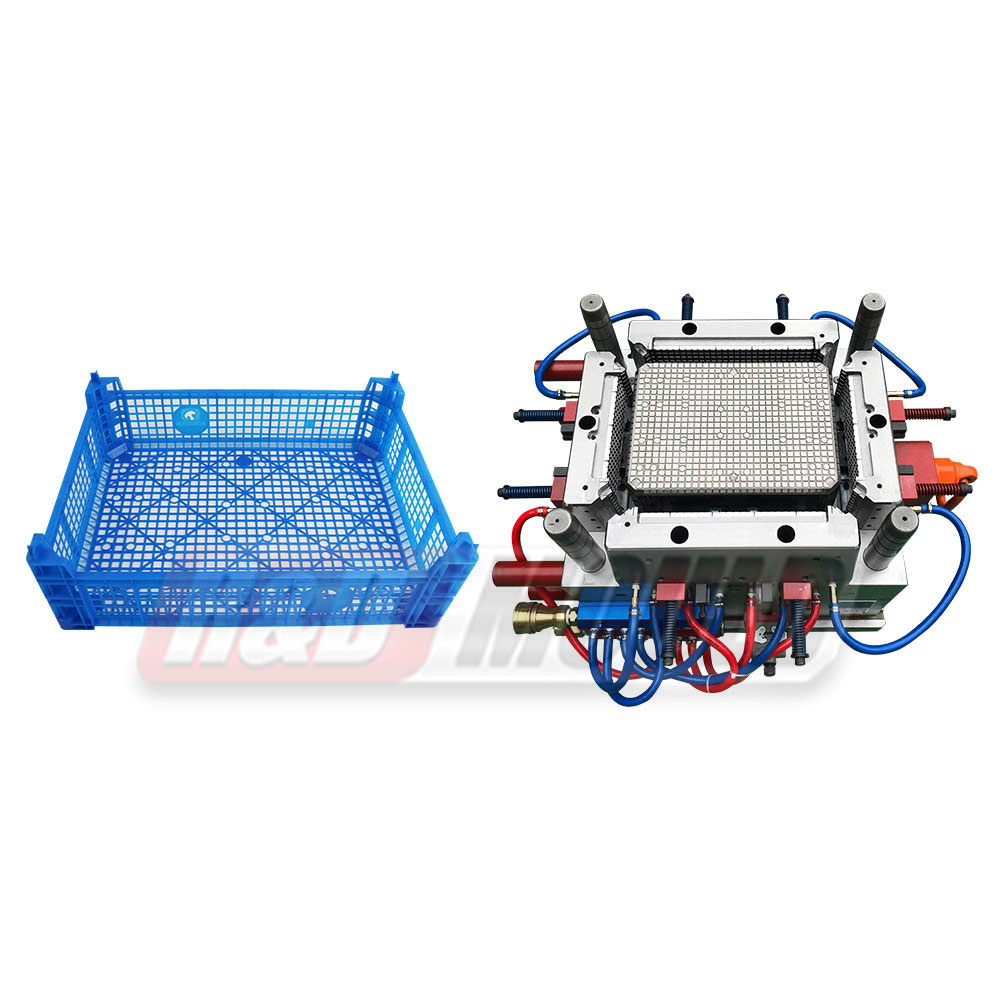
Plastic crate moulds are not one-size-fits-all. Different applications require different structures and mould approaches. Common classifications include collapsible crate moulds, bottle crate moulds, bread crate moulds, vegetable crate moulds, fish crate moulds, milk crate moulds, and industrial crate moulds.
Each type brings its own design focus. Bottle crates require stable internal partitions. Vegetable and fish crates need smooth surfaces for easy cleaning. Industrial cratesemphasisee load capacity and stacking stability.
A Crate Mould must reflect these usage differences through rib layout, wall thickness distribution, and handle structure design.
Steel Selection and Hardness Control in Crate Mould
Steel selection plays a major role in mould life and daily stability. For plastic crate moulds, choosing suitable steel for the mould base, core, and cavity is more important than simply selecting a hard material.
Hardness must be controlled within a reasonable range. Steel that is too hard may reduce machining accuracy and increase the risk of cracking under pressure. Balanced hardness supports steady injection under repeated cycles.
An experienced Crate Mould Manufacturer evaluates steel choice based on crate size, expected cycle time, and production rhythm rather than relying on a single standard material.
.jpg)
Precision Machining and Moving System Accuracy
Crate moulds often include large moving parts and guiding systems. These areas require high-precision machining. Any deviation can cause uneven movement, surface wear, or alignment issues during mould opening and closing.
Hand processing in critical moving areas is generally avoided. High-precision machines provide consistency that manual work cannot match. This precision supports stable mould operation over years of use.
For large crate moulds, guide pin alignment and slider movement accuracy directly affect surface quality and demoulding smoothness.
Handle Area Design and Venting Importance
The handle area of a plastic crate is a key stress point. When a loaded crate is lifted, force concentrates around the handles. Poor mould design in this area often results in visible weld lines or weak spots.
A well-planned exhaust system in the handle area allows air to escape smoothly during injection. Without proper venting, the melt flow may form visible welds that reduce structural strength.
This detail is often overlooked in early design but becomes critical during real-world use. A reliable Crate Mould Manufacturer treats handling venting as a core design task, not a minor adjustment.
A Crate Mould is more than a forming tool; it defines how a crate performs throughout its service life. When structural strength, handle design, venting, and machining accuracy are aligned, crates maintain their function under repeated loading and transport.
By working with a Crate Mold Manufacturer that understands real application demands, factories can move from design to stable production with clearer expectations and fewer structural issues over time.



 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español Français
Français