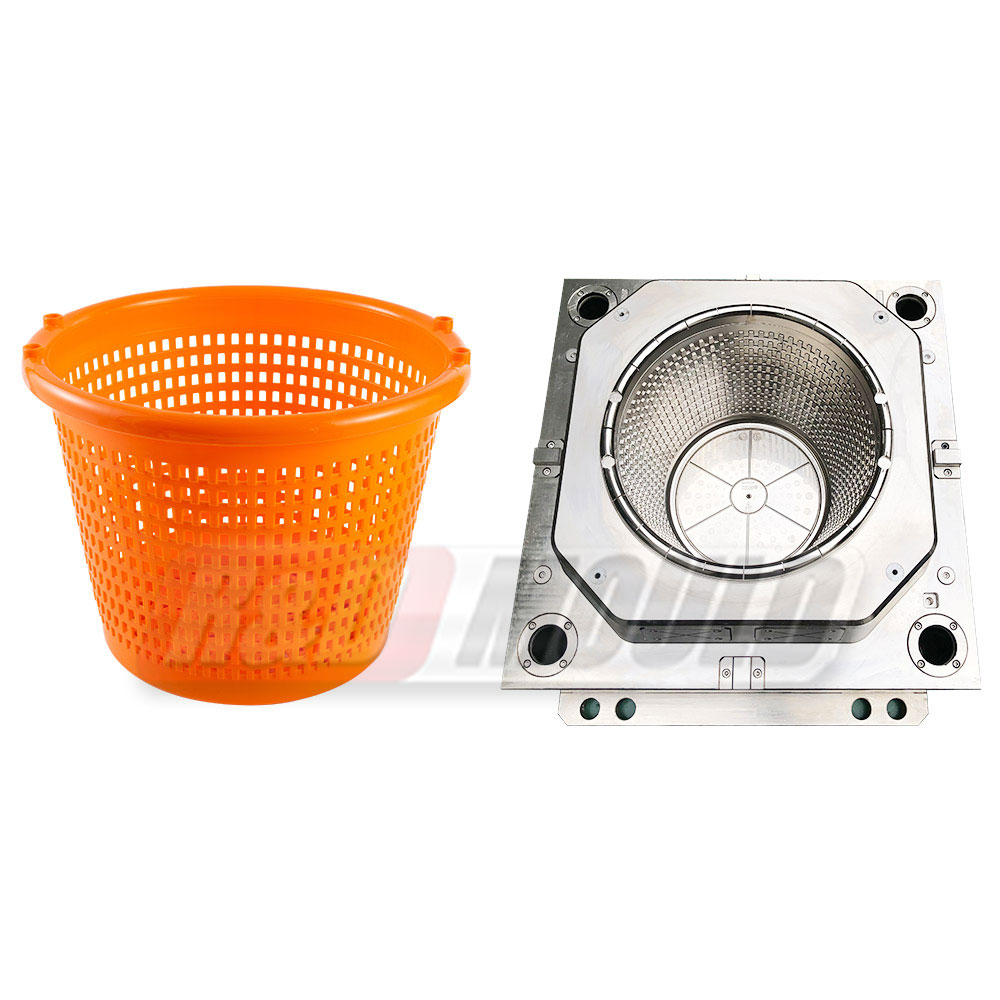
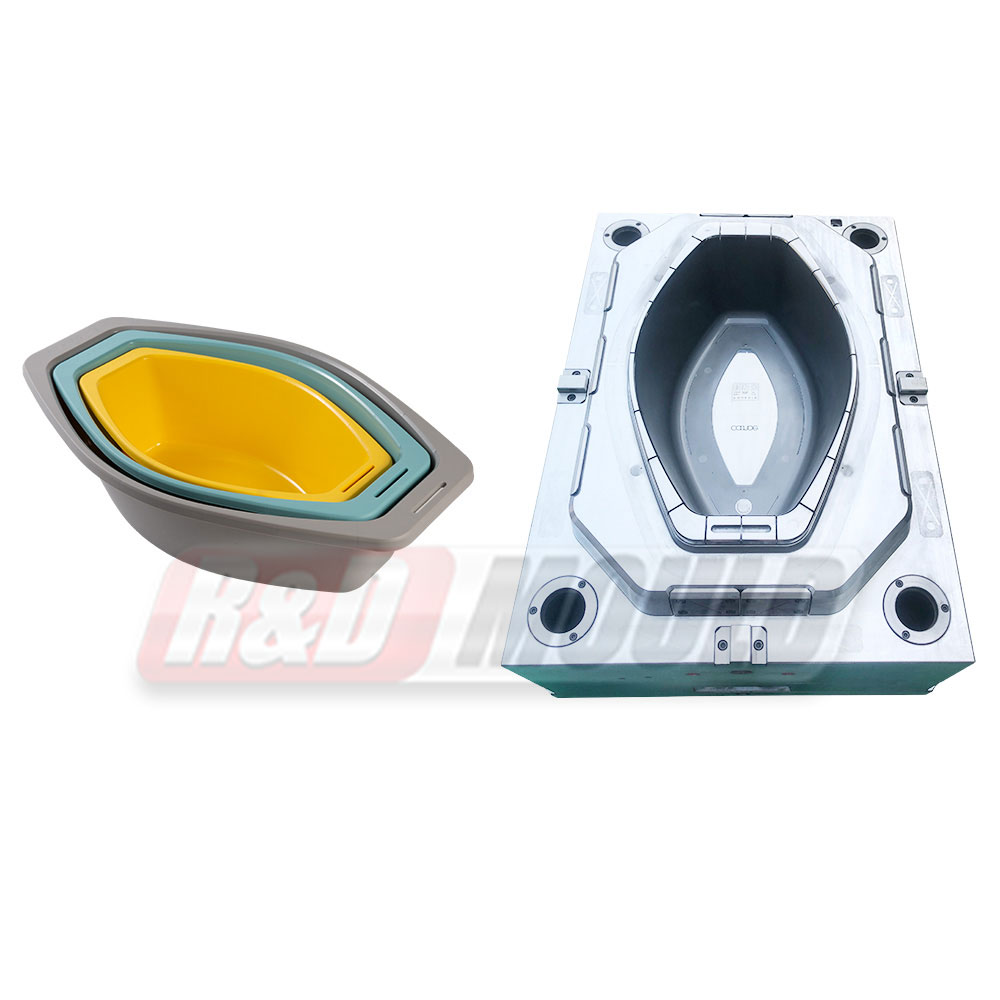
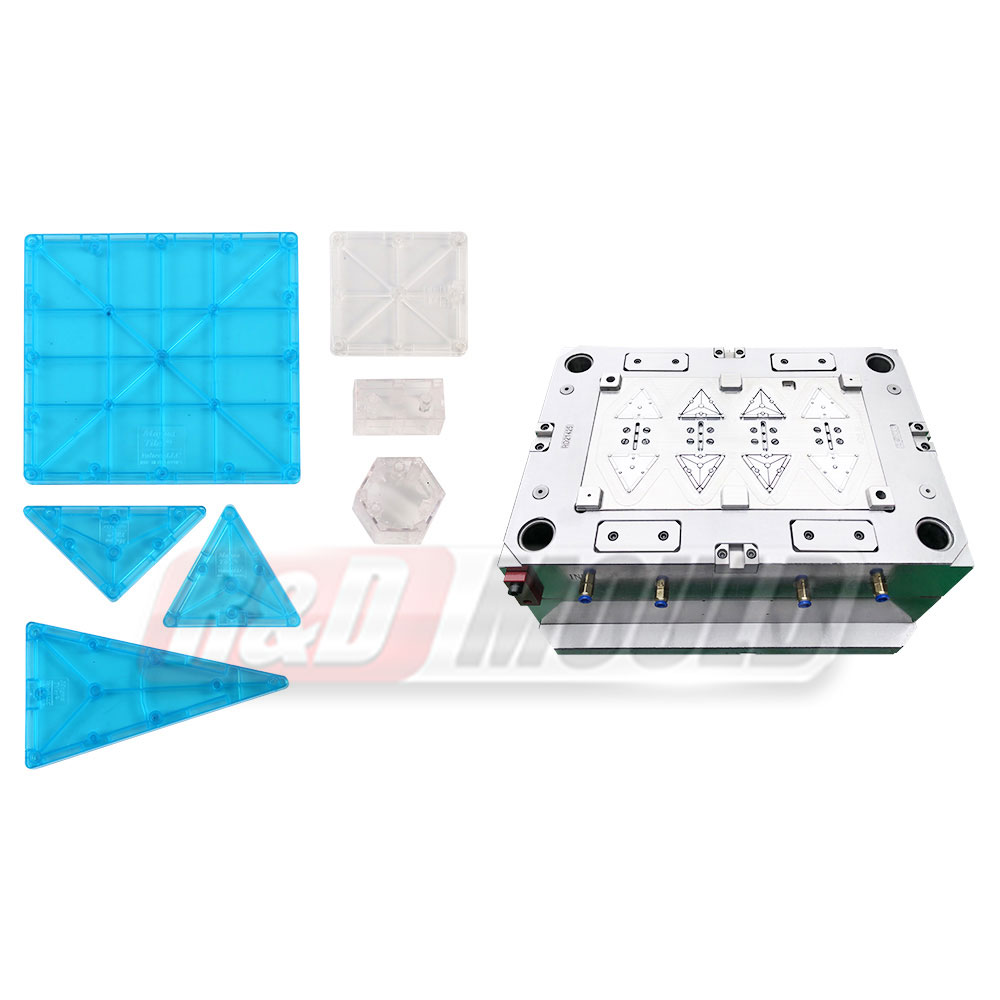
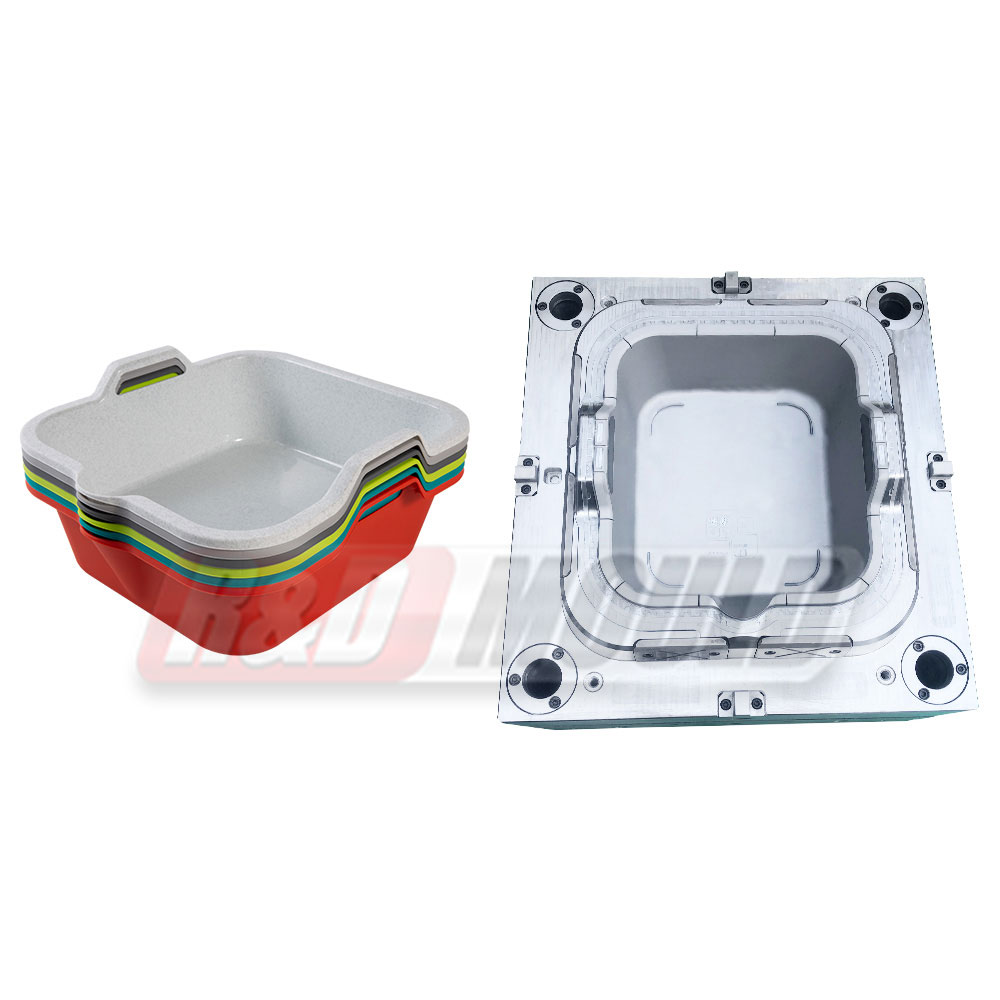
SMC Mould production follows a compression molding process that focuses on pressure and temperature coordination. Preheated molding material, such as SMC or BMC, is placed into a preheated open mold. After closing the mould, higher pressure pushes the material to flow and fill the cavity. Under controlled temperature, the material gradually solidifies, and the product is then removed for auxiliary processing.
This forming method avoids long flow paths found in other processes. Material moves in multiple directions with relatively uniform pressure, which helps maintain shape consistency. For products where dimensional stability matters, SMC Mould structure supports lower internal stress and a steady surface appearance. SMC Mould Manufacturers usually treat process control as part of mould design rather than leaving it entirely to machine settings.

Because there is no pouring system, raw material usage stays efficient. This feature is often valued in continuous production, where material cost control is part of daily operation.
Why Temperature and Pressure Matter in SMC Mould Design
Temperature and pressure directly influence how SMC material behaves inside the mould. Too much variation can affect surface quality or create uneven thickness. For this reason, SMC Mould development involves careful review of molding temperature, pressing pressure, and holding time.
Rather than relying on fixed values, parameters are selected after considering product shape, wall thickness, and material type. Thin-wall products, in particular, benefit from balanced pressure distribution. Short flow distances reduce deformation and help the product keep its intended form after demoulding.
SMC Mould Manufacturers often work with compression molding machines to match mould structure with press capacity. This coordination supports a stable production rhythm and reduces the need for frequent parameter changes during operation.
Structural Advantages of SMC Mould in Complex Products
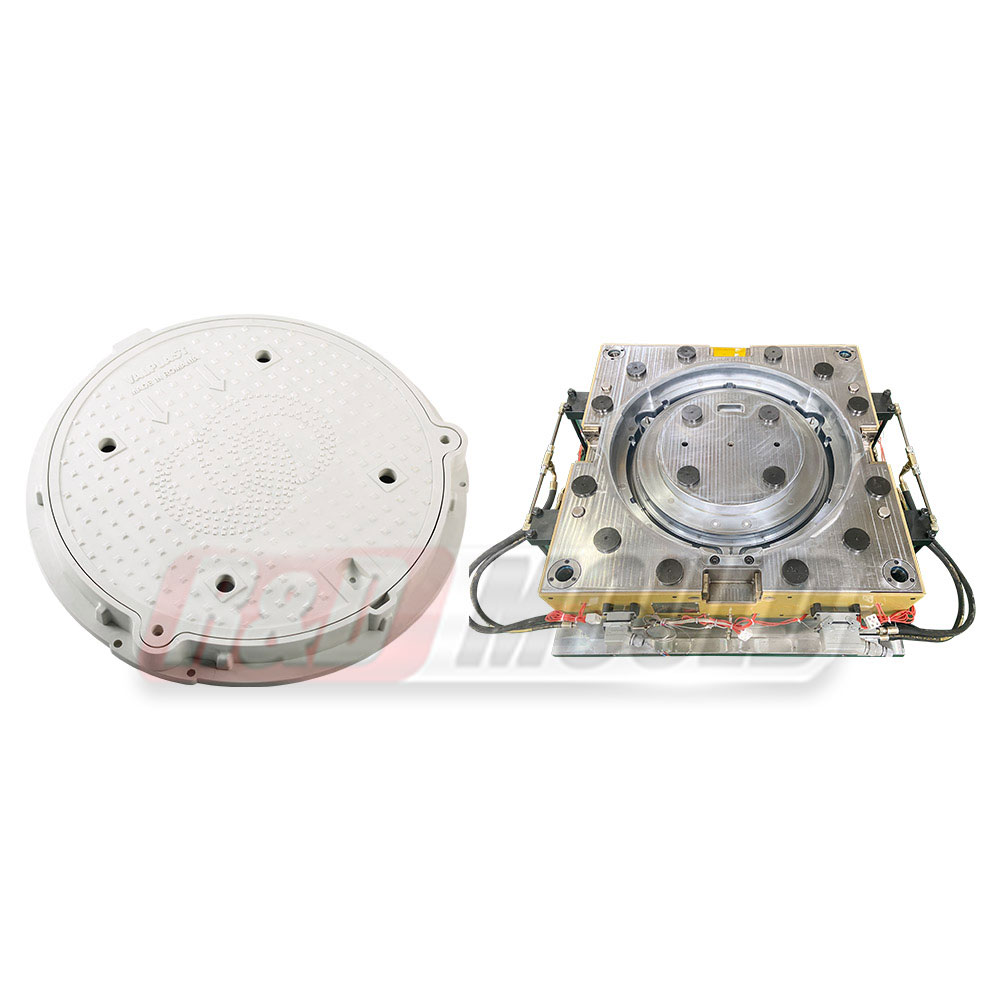
One key feature of SMC Mould is its ability to form products that are wide, flat, or pot-shaped without warping. The uniform cavity pressure supports even material distribution across large surfaces. This makes the mould suitable for applications such as integral residences, seats, and manhole covers.
Multi-directional material flow also helps reduce internal stress. Products maintain their shape after cooling rather than shifting or bending over time. This behavior is useful for components that need to fit into assemblies without secondary correction.
.jpg)
SMC Mould structure supports thin-walled designs that are difficult to achieve with other forming methods. With controlled compression and solidification, the mould can shape detailed surfaces while keeping wall thickness consistent.
How SMC Mould Manufacturers Support Application Needs
SMC Mould Manufacturers focus on aligning mould design with application requirements. For automotive parts such as bumpers, seats, and front grilles, mould rigidity and cavity accuracy support repeatable output. For infrastructure-related products like manhole covers, uniform pressure and stable shape retention are key considerations.
During mould development, attention is given to cavity layout, venting, and heating zones. These elements influence how material fills and cures under compression. Testing under real press conditions allows observation of flow behavior and surface finish.
An SMC Mould built with proper structure and parameter coordination becomes a stable tool in compression forming. By combining material behavior understanding with practical mould design, SMC Mould Manufacturers support consistent product shape, controlled internal stress, and steady production across different application fields.



 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español Français
Français